Before going for an HIV Test you must see some early signs of HIV in yourself. Like any other disease, HIV also shows some early symptoms. The symptoms could vary person to person and can be different for Men & Women. Although, some people don’t show any symptoms at an early stage and only experience symptoms when they progress towards AIDS.
It is always good that the infection should be detected early so that you receive a prompt treatment to control the virus. Controlling the virus may possibly slow the progression into AIDS.
You should not rely on Symptoms to ensure if you’re an HIV+ or not. The only way to be sure is to get tested. If you live in the United States, you may count on STDCheck (A chain of STD Testing Clinic). They offer a wide range of STD tests including the HIV RNA Test, which is the only FDA-approved test in the United States to detect HIV early just after 9-11 days of exposure. Other HIV tests may take up to 3 months to detect HIV based on Window Period. To know more about the HIV RNA Test or to order a test for you, you can visit STDCheck.Com
This article will help you understand some early signs of HIV in Men & Women.
When we talk about Men with HIV, 2/3 of Gay and bisexual men have found HIV+ in the United States. Black/African American men are also highly affected.
2 out 3 Women who got infected with HIV is due to unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner. As HIV sometimes don’t show any symptom at an early stage, people with HIV pass the virus to their partner without any intention. If you’re having sex with a new partner whose status is unknown, you must use some protection before having sex.
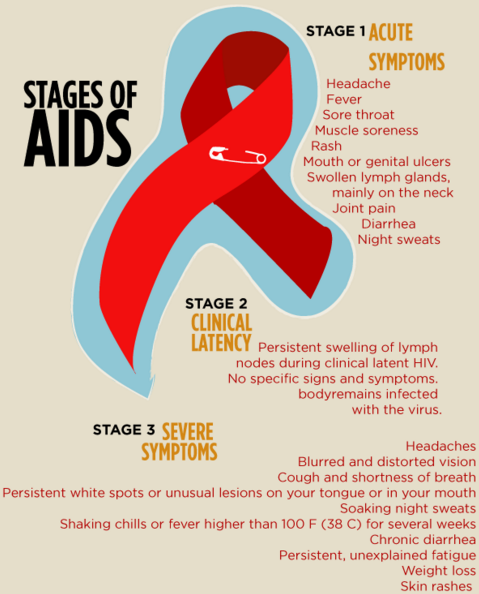
After 2-4 weeks of infection, some people, not all start feeling some flu-like symptoms. These symptoms may go away after few weeks. This flu described as “worst flu ever.” This is the first stage of HIV infection also called as acute retroviral syndrome (ARS).
Early HIV Symptoms may include
- Fever
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Rash
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint aches and pains
- Swollen glands
- Sore throat
- Ulcers in the mouth or on the genitals
- Night sweats and diarrhea
Even if you’ve some symptoms mentioned above, don’t assume you’ve been infected with HIV. These symptoms could be caused by other illness. The only way to be sure is to get tested.
If you have any of the symptoms, It is highly recommended that you should get tested for HIV. It is possible that you may have more than one sexually transmitted diseases at a time. To know your status, you should take STD panel test along with HIV Early Detection test. To know more about STD Testing & Pricing Click Here.
What Happen Next?
After the early stage of HIV is over, the disease moves into a stage called clinical latency stage, and if you don’t take any HIV treatment in this stage, its progression into AIDS starts.
What is Clinical Latency Stage?
After the early stage of HIV, the HIV disease moves into clinical latency stage. During this stage, people with HIV show no symptoms or very mild ones.
The doctor may prescribe you take antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is an HIV treatment which keeps HIV in check. With antiretroviral therapy (ART) someone can live healthy for several decades. Although if someone is not on antiretroviral therapy (ART), the clinical latency stage may last about 10 years and sometimes be earlier.
Someone can still pass HIV to others during this stage.
Progression into AIDS
HIV virus starts weaken your immune system and you progress to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Usually, this stage happens when you’re not on antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is the late stage of HIV infection.
During progression stage you may feel symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea
- Sores of the mouth, anus, or genitals
- Memory loss
- Recurring fever
- Night sweats
- Extreme tiredness
- Red, brown, pink, or purplish blotches on or under the skin or inside the mouth, nose, or eyelids
- Depression
- Pneumonia
Most of the symptoms of progression stage come because of opportunistic infections. Your body’s immune symptoms got damaged and you got hit by other infections very easily.
Lower Your Risk of Getting HIV
You can reduce the risk of getting an HIV substantially by doing these things
- Use less risky sexual behavior: Anal sex is highly risky that is why Gays & Bisexuals got an HIV easily. Oral sex is less risky than vaginal sex.
- Use of condom lowers the risk of having HIV. Always use a condom when you have sex with a person whose status is unknown.
- Don’t sex with more than one people: Having sex with more than one people always put you at risk of having an HIV.
- Educate Yourself: Getting yourself educated about HIV risks and how you can reduce it, is the best way to prevent yourself against an HIV.
- Talk to your doctor about pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP): PrEP is a new HIV prevention method. People who don’t have an HIV can take a pill daily to reduce their risk of getting an HIV.
- Get tested for other STDs: If you’re sexually active, get tested at least once a year. Get tested for other STDs also and not only for HIV. You may go for a panel test that includes 10 tests for common sexually transmitted diseases.
- If your HIV partner to take HIV Treatment: If your partner is HIV+, ask your partner to be on antiretroviral therapy (ART).